This section will provide you with a better understanding of title insurance, including:
What is the Importance of Title Insurance? What is the Basic Function of a Title Company?
Who Needs Title Insurance?
What is the Difference between Title Insurance and Casualty Insurance?
What Does Title Insurance Insure?
What if I am Buying Property from Someone I Know?
20 Reasons for Title Insurance
What are Some Common Title Clearance Problems to be Aware of?
Help Us Stay on Top of Your Transaction!
What is the Typical Life of a Title Search?
What is the Importance of Title Insurance?
The purchase of a home is usually the most expensive and long-term financial undertaking an individual or family ever makes, therefore it is very important to fully protect the investment. You and your mortgage lender will want to make sure the property is indeed yours, and that no one else has any lien, claim or encumbrance on your property.
Safe, sound and reliable title insurance provides the basic home ownership protection you need.
What is the Basic Function of a Title Company?
The basic function of a title insurance company is to take steps to minimize the risk that a policyholder will suffer any loss, or be subject to, any adverse claim, as well as to safeguard his ownership of, or claims in, the property. If title problems do arise in spite of this preventative work, title insurance will pay for the costs of defending against an attack on the title as insured, as well as any valid claims.
Who Needs Title Insurance?
Buyers and lenders in real estate transactions need title insurance. Both want to know that the property they are involved with is insured against certain title defects. Title companies provide this needed insurance coverage subject to the terms of the policy. The seller, buyer and lender all benefit from the insurance provided by title companies.
What is the Difference between Title Insurance and Casualty Insurance?
Title insurers work to identify and eliminate risk before issuing a title insurance policy. Casualty insurers assume risks.
Title insurance will indemnify you against loss under the terms of your policy, but title companies work in advance of issuing your policy to identify and eliminate potential risks, preventing losses caused by title defects that may have been created in the past.
Title insurance also differs from casualty insurance in that the greatest part of the title insurance premium dollar goes towards risk elimination. Title companies maintain “title plants”, which contain information regarding property transfers and liens reaching back to the time of “recordkeeping” by the County Recorder. Maintaining these title plants, along with the searching and examining of title, is where most of your premium dollar goes.
Casualty insurance companies work in a very different manner. Casualty insurance companies realize that a certain number of losses will occur each year in a given category (auto, fire, etc.). The insurers collect premiums monthly or annually from the policy holders to establish reserve funds in order to pay for expected losses.
What Does Title Insurance Insure?
Title insurance offers protection against claims resulting from various defects (as set out in the policy), which may exist in the title to a specific parcel of real property, effective on the recording date of the documents. For example, a person might claim to have a deed or lease giving them ownership or the right to possess your property. Another person could claim to hold an easement giving them a right of access across your land. Yet another person may claim that they have a lien on your property securing the repayment of a debt. That property may be an empty lot, or it may hold a 50-story office tower, title companies work with all types of real property.
What If I am Buying Property from Someone I Know?
You may not know the owner as well as you think you do. People undergo changes in their personal lives that may affect title to their property. People get divorced, change their wills, engage in transactions that limit the use of the property, and have liens and judgments placed against them personally for various reasons.
There may also be matters affecting the property that are not obvious or known, even by the existing owner, which a title search and examination seeks to uncover as part of the process leading up to the issuance of the title insurance policy.
Just as you wouldn’t make an investment based on a phone call, you shouldn’t buy real property without assurances as to your title. Title insurance provides these assurances.
The process of risk identification and elimination performed by the title companies, prior to the issuance of a title policy, benefits all parties in the property transaction. It minimizes the chances that adverse claims might be raised, and by doing so, reduces the number of claims that need to be defended or satisfied. This process keeps costs and expenses down for the title company and maintains the traditional low cost of title insurance.
20 Reasons for Title Insurance:
1. Title insurance will protect you against a loss on your home or land due to a title defect.
2. Claims have risen dramatically over the last 30 years.
3. Claims constantly arise due to marital status and validity of divorces.
4. A deed or mortgage may have been made by an incompetent or under-aged person.
5. A deed or mortgage made under an expired Power of Attorney may be void.
6. A deed or mortgage may have been procured by fraud or duress.
7. A deed or mortgage may have been made by a person with the same name as the owner.
8. A child born after the execution of a will may have interest in the property.
9. Title transferred by an heir may be subject to a federal estate tax lien.
10. An heir or other person presumed dead may appear and recover the property or an interest.
11. A judgment regarding the title may be voidable because of some defect in the proceeding.
12. By insuring the title, you can eliminate delays when passing your title on to someone else.
13. Title insurance reimburses you for the amount of your covered loss.
14. Title insurance helps speed negotiations when you’re ready to sell or obtain a loan.
15. A deed or mortgage may be voidable if signed while the grantor was in bankruptcy.
16. There may be a defect in the recording of a document upon which your title is dependent.
17. Title insurance covers attorney fees and court costs.
18. Many lawyers protect their clients as well as themselves by procuring title insurance.
19. A title policy is paid in full by the first premium for as long as you own the property.
20. Conveyances and proceedings affecting rights of military personnel protected by the Soldiers’ and Sailors’ Civil Relief Act.
What are Some Common Title Clearance Problems to be Aware of?
The following items may require added clearance and processing time for title and escrow.
Avoid delays by providing information on your current transaction to title and escrow regarding any of the items listed below:
• Establishing fact of death – i.e., Joint Tenancy
• Power of Attorney
• Physical inspection results, encroachments, or off-record easements known to you
• Liens and judgments known to you
• Child/spousal support liens known to you
• Probates affecting your property
• Bankruptcies affecting your property
• Transfer/loans involving corporations/partnerships on your property
• Last minute changes in buyers
• Last minute changes in type of coverage
• Recent construction
• Family trusts affecting your property
• Business trusts affecting your property
• Property recently foreclosed

Help Us Stay on Top of Your Transaction!
Will any of these situations affect your transaction?
• Is this a short sale?
• Is this an REO?
• Are your principals exchanging (1031) this property?
• Will your principals be using a Power of Attorney?
• Are any of the parties on title deceased?
• Has there been a change in marital status?
• Is there, or will there be a new entity formed? i.e., Partnership, LLC or any other type of corporation
• Are the sellers of this property non-residents of California?
• Is the property held in a trust?
• Has the Statement of Information (SI) been returned to escrow?
• Will the property be sold in 2-4 years?
• Has a bankruptcy and/or a discharge been filed?
• Are there loans showing on the prelim that should have been reconveyed?
If you answered “YES” to any of these questions, please call your Progressive Title Representative.
• Do all parties signing documents have a valid photo ID or driver’s license? (Note: If “NO”, now is the time to apply for a valid ID.)
*Please Note: This is a “short list”. Call your Progressive Title Representative if you have additional information that you think may be important, or if you have any questions.
What is the Typical Life of a Title Search?
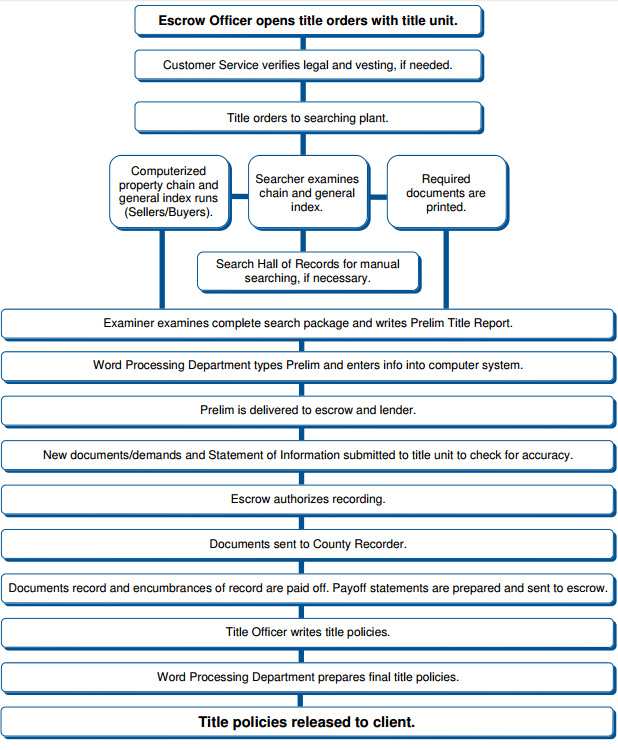
Title Policies
This section will help you to better understand:
What Types of Policies are Available?
How Do the CLTA and ALTA/CLTA Homeowner Policies Compare?
How Does the Interim Binder Work? What are Common Ways to Hold Title?
What Protection am I Obtaining with My Title Policy?
When is the Premium Due?
What are My Chances of Ever Using My Title Policy?
What are the Types of Ownerships and Properties that are Insured?
What Types of Policies are Available?
Title companies routinely issue two types of policies: An “Owner’s” Policy, which insures you, the homebuyer for as long as you and your heirs own the home and a “Lender’s” Policy, which insures the priority of the lender’s security interest over claims that others may have in the property. There are various types of policies issued to an “owner” by title insurers in California.
The most common are:
California Land Title Association Standard Coverage-CLTA or “Standard Policy”:
CLTA Standard Policy provides title insurance coverage to:
• Owners and/or lenders with insurable interests in real property
• Basically, insures against loss or damage by reason of matters appearing in the public records, as defined therein
American Land Title Association/California Land Title Association Homeowner’s Policy (ALTA/CLTA Homeowner’s Policy) sometimes called the “HOP Policy”:
ALTA/CLTA Homeowner’s (HOP) Policy provides title insurance coverage to:
• Owners of improved one-to-four family residential property.
• Expands the number of covered title risks greatly, including certain specified risks that may arise in the future.
• Provides for payment of a “deductible” in some instances. Our most comprehensive policy, the “HOP” (ALTA/CLTA Homeowner’s Policy of Title Insurance) is automatically issued by Progressive Title and is our default policy on one-to-four residential property.
• The “insured owner”, however, must be a “natural person(s)”. A “natural person” is a real human being, i.e, individual or family trust, etc. as distinguished from a corporation, which is often treated at law as a fictitious person.
ALTA Owner’s Policy:
ALTA Owner’s Policy provides title insurance coverage to:
• Owners with insurable interests in real property
• This is usually requested as an “extended coverage” policy
Lender’s Policy:
Lender’s Policy provides title insurance coverage to:
• Lenders who finance real estate transactions
• Responds to lender’s concern for protection of investment
• Assures lender of the priority of their lien, and that the lien is valid and enforceable

Joint Protection Policies:
Joint Protection Policies are generally issued when a seller takes back a second deed of trust as part of the purchase price.
The Joint Protection Policy:
• Protects the buyer’s and lender’s interests under one policy
• Insures the interest of both the owner and the lender, avoiding paying two premiums
How Do the CLTA and ALTA/CLTA Homeowner Policies Compare?

Interim Binder:
As more and more people buy property for investment or speculation, the Interim Binder becomes an even more important tool. The Interim Binder is not, in itself, a policy of title insurance. However, when issued, it binds the insurer to issue a policy of title insurance within a specified period of time. By utilizing the Interim Binder, principals to a transaction can realize a substantial savings within the cost of title insurance.
HERE’S HOW IT WORKS
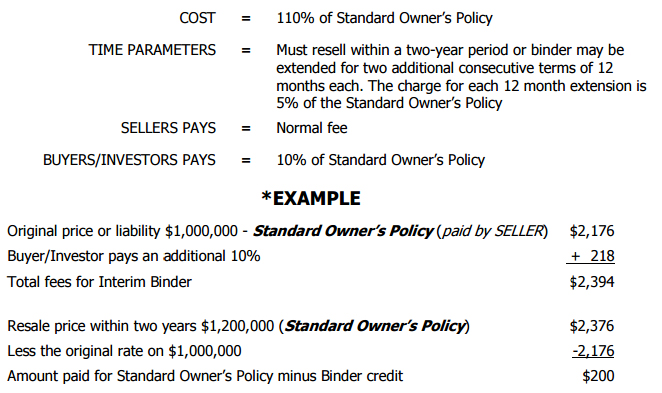
If a Homeowner’s Policy (HOP) is requested, add an additional 10%, $238, for a total of $438. The total cost to the buyer/investor is $656. By contrast, the rate the buyer/investor would normally pay for the HOP without utilizing the Interim Binder is $2,614.
The example above is provided for informational purposes only. Due to variables in liabilities, underwriters, and types of policies that may be issued, the pricing for your transaction may differ.

3 and 4 Year Interim Binder pricing available. Contact your Progressive Title Representative for more information.
Note: Progressive Title Company automatically issues the HOP Policy for single family 1 to 4 unit properties. The HOP Policy is the most current and comprehensive policy available by CLTA/ALTA for residential properties.
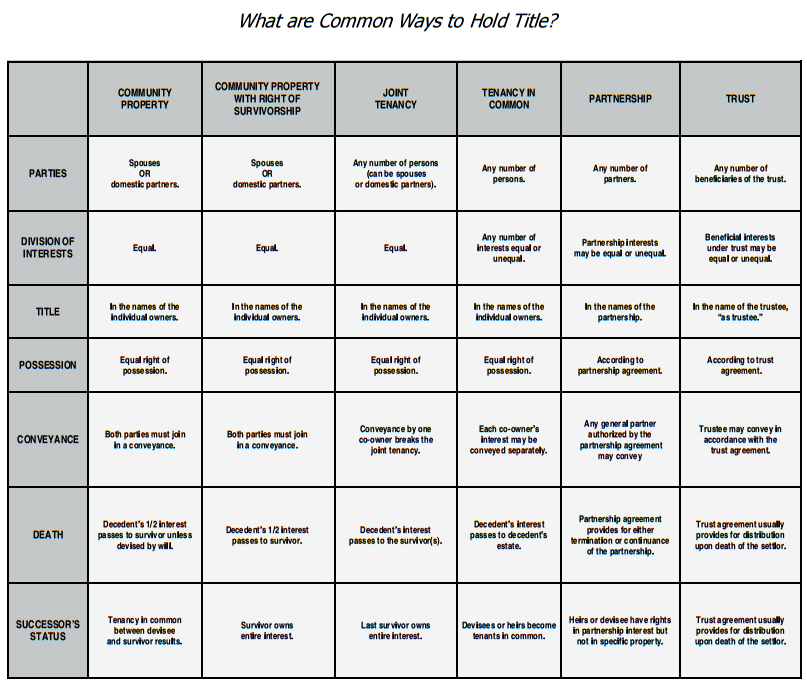
What Protection am I Obtaining with My Title Policy?
A title insurance policy contains provisions for the payment of the legal fees in defense of a claim against your property, which is covered under your policy. It also contains provisions for indemnification against losses that result from a covered claim.
When is the Premium Due?
A premium is paid at the close of a transaction. There are no continuing premiums due as there are with other types of insurance.
What are My Chances of Ever Using My Title Policy?
In essence, by acquiring your policy, you derive the important knowledge that recorded matters have been searched and examined so that title insurance covering your property can be issued. Because we are risk eliminators, the probability of exercising your right to make a claim is very low. However, claims against your property may not be valid, making the continuous protection of the policy all the more important. When a title company provides a legal defense against claims covered by your title insurance policy, the savings to you for that legal defense alone will greatly exceed the one-time premium.
What are the Types of Ownerships and Properties Progressive Title Insures?
Fee Estate
An estate under which the owner owns a complete interest in the property and is entitled to the unrestricted use and enjoyment of the property, including the right to dispose of the property.
• CLTA Standard Coverage Policy, ALTA Owner’s Policy and ALTA/CLTA Homeowner’s Policy are available for this type of ownership.
Condominium
A type of ownership in real property where all of the owners own their individual unit, together with an undivided interest in common areas, with the exception of the interior of the unit to which they have title.
• CLTA Standard Coverage Policy, ALTA Owner’s Policy and ALTA/CLTA Homeowner’s Policy are available for this type of ownership.
Planned Unit Development (PUD)
A type of ownership where individuals actually own the building or unit they live in, but common areas are owned jointly with the other members of the development. In contrast to a condominium, where an individual actually owns the airspace of his unit, common areas are owned jointly with the others in the development.
• CLTA Standard Coverage Policy, ALTA Owner’s Policy and ALTA/CLTA Homeowner’s Policy are available for this type of ownership.
Stock Cooperative (Co-Op)
A type of multiple ownership in which the residents of a multi-unit housing complex own shares in the stock cooperative corporation that owns the property, giving each resident the right to occupy a specific apartment or unit.
• CLTA Standard Coverage Policy and ALTA Owner’s Policy are available for this type of ownership.
Leasehold Estate
A way of holding title to a property wherein the lessee does not actually own the property, but rather has a lease on it for a specific amount of time.
• CLTA Standard Coverage Policy and ALTA Owner’s Policy are available for this type of ownership.
Types of Properties
Examples of types of properties we insure are Residential 1-4 Family, Residential Multiple Dwelling, Commercial, Agricultural, and Industrial.

 310.873.4188
310.873.4188